Author/Editor: Dr Farhat Naz (Consultant Physician)
Diabetes self care/ definition, practices, advantages and remote care
1.What is diabetes self-care?
Diabetes self-care is the practice of educating the diabetic patients to learn how to take care and manage diabetes at their own. This concept is now getting increasing popularity and being developed and practiced by many health care professionals. As it is the responsibility of every healthcare professional to educate the patient that diabetes is a disease with no permanent cure but it can be managed and the complications of diabetes can be delayed or prevented by having good medical care and healthy life style practices.
So, if broadly classified, the care of a diabetic patient relies on two main pillars.
1. Medical care by healthcare professional.
2. Self care by the patient.
2.Why diabetes self-care is important?

The burden of diabetes is growing worldwide and diabetes which was initially considered the disease of high socioeconomic communities is now rapidly involving medium and low socioeconomic communities. This rapid paradigm shift has now left a huge economic burden on health sector and many third world countries find it impossible to provide optimum care to each diabetic patient according to standard management guidelines and protocols.
Diabetes self care empowers a diabetic patient to take control of the disease by having a good knowledge of practices helpful in managing diabetes and earlier recognition of acute and chronic complications of the disease.
3.What practices are involved in Diabetes Self Care?
Though the knowledge of Diabetes from patient’s point of view, and aspects of management are diverse, as multiple factors are involved in it, but there are 7 basic components of Dibetes Self Care as determined by American Diabetes Association (ADA).
1.Healthy eating
Healthy eating refers to “a pattern of eating a wide variety of high quality, nutritionally-dense foods in quantities that promote optimal health and wellness.” The behaviors surrounding when to eat, what to eat, and how much to eat are influenced by a complex set of factors, including food and cultural preferences, food security, health beliefs, and eating habits, individuals with diabetes can develop meal plans that focus on macronutrient quality, healthy eating patterns, metabolic goals, and personal food preferences.
Through discussion and problem solving with health care team, individuals with diabetes and related conditions can learn how to integrate healthy and safe eating patterns into their daily lives.

As defined by the Dietary Guidelines 2015-2020, a healthy eating pattern contains a combination of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, low-fat dairy, proteins, and oils while decreasing intake of sodium, added sugars and saturated fats.
Diabetic individuals should develop habit of tracking consumed food for calories, carbohydrate, fat and protein content. Controlled caloric intake and healthy diet plan can improve blood glucose, LDL cholesterol and HbA1C.
The ability to read the food labels and calculate caloric intake can promote healthy eating and drinking decisions that lower cardiovascular risk and improve glycemic control.
/**/2.Exercise/ Physical activity:
Being active is inclusive of the duration and intensity of daily physical movement as well as routine activities. The benefits of regular physical activity on health are remarkable and diabetics are not exception to that. Diabetic patients should perform routine physical activities as well as planned physical activities. Strenuous exercise is not essential and a regular walk will suffice for most of the patients to achieve the goals.

Diabetes health professionals can assess and monitor the activity level and make a plan to address any barrier limiting the activity of the patient.
3.Self monitoring:
All the diabetics should be advised to perform home glucose monitoring with gluco-meter and should be educated to use the device properly. They should test their blood glucose at least once a day. They should chart the readings for healthcare visit. They should be well aware of symptoms of high and low blood sugar and how to manage the fluctuations in blood glucose without the help of doctor. The patient should increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring and should we able to know when and how to contact a healthcare facility if failed to manage the condition him/herself.
Self Monitoring in diabetes is multidirectional and includes the following:
- Monitoring blood glucose
- Monitoring blood pressure
- Activity
- Nutritional intake
- Weight
- Medications
- Feet/skin care
- Mood and sleep
- Symptoms like shortness of breath
- Neurological symptoms like dizziness/ numbness/ weakness etc.
- Eye sight/vision
The record of Self monitoring is essential and patients can use paper to record data or can use the latest technologies to record healthcare data and prevent errors. These technologies include connected devices and mobile apps for self monitoring.
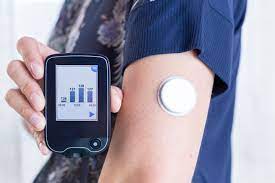
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) has transformed intermittent monitoring to monitoring in real time.
4. Compliance with medication:
Medications are essential for management of diabetes. Improper use of medicine will leave to failure to achieve therapeutic goals. The compliance with medication, the drug response, side effects of treatment and cost are the challenges faced by the patient and healthcare provider. The doctors should educate the patient regarding benefits and risks of the drugs and emphasize the importance of each drug and health risks in case of non-compliance. The patient should be advised to follow prescription and avoid changing the dose or duration without consulting the doctor.

Shared decision making and collaboration with patient will enhance patient’s compliance, diabetes control and prevention of complications.
5.Problem solving
Problem solving is an essential skill of diabetes self care and it is the ability of the patient to identify problem and develop solution for it. For example if the patient is feeling excessive hunger, sweating, palpitations the patient should be aware of low blood sugar and should check blood glucose and take some sweet or candy. On the other hand feeling of excessive thirst and increased urination is indicator of high sugar. Patient should re-visit the diet and should be able to adjust medication before visting the doctor.

At the most basic level, problem solving is a process that involves 3 steps:
(1) Identify the problem,
(2) Think appropriate solution
(3) Apply and evaluate the solution.
The ability to solve problem is associated with improved A1C and lower risk of complications. Problem solving skill is particularly effective in low income urban and rural communities. If patient develops the problem solving ability, it removes burden on health care system.
6. Healthy coping
Healthy coping is the cornerstone of diabetes self care. It is defined as positive attitude towards diabetes management. Only those patients will be able to successfully adopt self care activities who think positive about their disease. Negative emotions, depression and anxiety, commonly associated with diabetes will adversely affect self care. Similarly the patients with memory issues will not be able to optimize self care activities. So healthy coping will involve the following components:
- self efficacy (the ability to perform self care activities)
- meditation (deep thinking practice that connects mind and body)
- good relations (Developing healthy relation with friends and family)
- seeking support ( Getting support from diabetes educator, healthcare provider, family and friends)

Healthy coping is critical for achieving successful self-care leading to good physical and psychological well-being.
Negative attitude towards the disease, depression and anxiety, thinking negative of the high demands related to self-care activities will lead to poor management and outcome of the disease. Self care related emotional burden and disease
7. Reducing risk:
Reducing risk refers to identifying diabetes related risks and taking measures to overcome the condition. These risks are either related to acute complications of diabetes like hypoglycemia (low sugar), or ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemia (high sugar).
The chronic risks are related to complications involving eyes, kidneys, heart/ blood vessels, nervous system and skin related conditions.
Early lifestyle modifications, weight loss, exercise and diet at pre-diabetes level can significantly improve adverse outcomes and be helpful to achieve therapeutic HbA1C levels, fasting and random blood glucose and target LDL. Achievement of these therapeutic goals is associated with delayed complications.

Adequate sleep is also mandatory to achieve good diabetes control. Depression, anxiety, legs cramps, low and high blood sugar impair sleep leading to increased A1C and blood glucose. Patient should adopt remedies to improve sleep. Another important lifestyle modification is to quit smoking and alcohol intake. Diabetics should connect to each other through social media platforms, share their experiences and help motivating each other.
Active participation in self care depends on:
(1) Knowing the value of preventing health problems.
(2) Recognizing the power of individual behavior to change health outcomes.
The data generated by the patients showing blood glucose monitoring, diet and lifestyle modifications can actively involve the patient, they take interest in their lab reports and know how to address their health concerns with the doctor leading to improved outcome.
4.What role social media and digital platforms can play in diabetes self care?

A systematic review on use of social media and digital platforms has concluded that diabetic patients can adopt use of social media and digital platforms to get knowledge of self care behaviors and this practice is expected to develop more in future.

Another tool to help diabetics to learn about Self Care is through mobile Apps. In a study conducted on features of mobile Apps in learning and practicing diabetes self-care, it was concluded that most Apps focused on diet, exercise, self glucose monitoring and compliance with medications but failed to address problem solving, healthy coping and reducing risk.
The use of technology has the capability to lower the cost of diabetes but extensive awareness is needed in this regard.
5. What are current technologies to support self care?

- Medical devices such as glucose meters, insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors.
- Digital therapeutics such as mobile apps
- Text messaging/ social media groups
- Electronic communications, and videoconference platforms.
- Wearable technologies, such as smart watches.
6. Can Diabetic patients receive health care remotely:
Diabetic patients can only adopt self care behaviors when they get proper guidance and motivation through healthcare provider. Diabetic patients can receive healthcare advice remotely through internet or mobile phones. The information can be conveyed to patient in simplified and easy to follow manner. A user friendly self care format will be helpful to educate and motivate the patient.
Shortly, technology driven healthcare system can help the Diabetic patients to optimize the disease care and improve outcome.
Shortly, education of a diabetes patient regarding self care is the part of diabetes management and it has the potential to remove huge health care burden and cost. Diabetes education programs should be part of government policies and education and support should be provided from community to primary and tertiary healthcare levels.
The use of artificial intelligence in monitoring diabetes self care activities and providing guidance at doorstep is the goal to be accomplished in near future. The education programs should be as effective in developing countries as in developed communities. The only solution to huge economic and health care burden caused by diabetes is active involvement of the patients through education and healthcare support.

