By: Dr. Farhat Naz
Co-author: Dr. Sadia Rehman
Definition
classification
Causes
Manifestations
Investigations
Management
What is diabetic foot?
Diabetic foot is any pathology related to feet in a diabetic patient as a consequence of complications of Diabetes.
The two major complications of diabetes are sensory neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease, the occurrence of diabetic foot is mostly related to sensory neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease or both.
How diabetic foot is classified?
Usually the diabetic foot can be categorized to five stages, ranging from normal foot, high risk foot, ulcerated foot, infected foot and necrotic foot. Though different classifications of diabetic foot are in practice but Wagner’s clasification divides diabetic foot into 5 grades:
- Grade 1: Superficial ulcer
- Grade 2: Deep full skin thickness ulcer
- Grade 3: Deep abscess/ osteomyelitis
- Grade 4: Partial gangrene of forefoot
- Grdae 5: Full foot gangrene
What are causes of diabetic foot?
A. Diabetic Neuropathy:
Diabetic patients develop dysfunction of peripheral nerves leading to decreased ability to feel pain. This will lead to blistering and ulceration in response to pressure and trauma. Minor injury or trauma can cause complications as they remain un noticed by the patient due to lack of pain. Almost two third of diabetic foot ulcers are related to sensory nerve damage.
B. Peripheral Artery Disease:
Most of diabetic patients have lipid abnormalities causing fats deposition in blood vessels leading to narrowing of vessels(diabetic angiopathy). This will lead to dcreased blood flow due to peripheral arterial disease. The feet will initially become cold and later discoloration (gangrene) will develop due to necrosis of tissue, this will eventually lead to amputations.
Around half of the patients with diabetic foot have combined nerve damage and peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Lifetime risk of developing diabetic foot is around 15-25%.
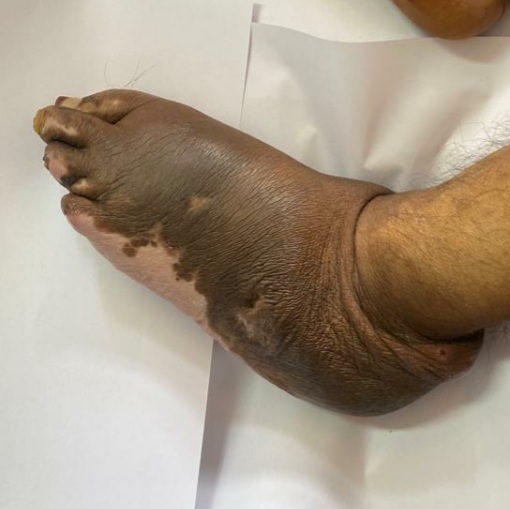
What are different manifestations of diabetic foot?
The diabetic foot can present as:
A. Diabetic blisters
B. Diabetic ulcers
C. Infections
D. Joint destruction (Arthopathy)
E. Gangrene
What is diabetic blister?
Blisters may appear spontaneously on diabetic feet and are clear, painless and without redness. These are mostly benign and have sterile fluid inside. They mostly heal spontaneously in 4-5 weeks. Antibiotics and steroids cream may be prescribed to prevent itching and infection.
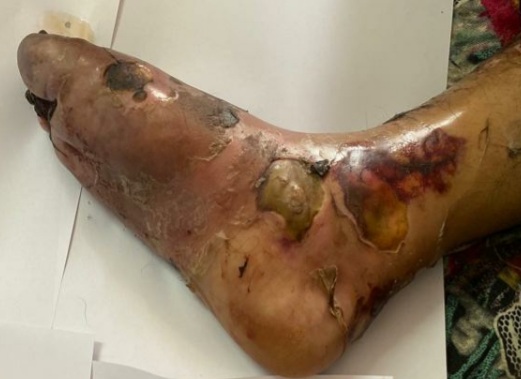
What is diabetic foot ulcer?
Ulcers are lesions which occur due to a beak is skin of a diabetic patient. It is one of the most common complications of uncontrolled diabetes. Ulcers usually develop in weight bearing areas of feet due to pressure effect from ill fitting shoes. As the patient cannot feel pain due to nerve damage, small ulcers initially go unnoticed. if the feet are not examined regularly and ulcers not treated in time, further complications may develop. The lesion will deepen to involve the bone (osteomyelitis) and will become infected.
How diabetic foot infection will present?
Infection will mostly occur in pre existing diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetic patients have poor neutrophilic response to infection. if blood sugar is high, the foot infection will be difficult to heal. If the patient has poor blood supply due to vascular disease, the infection will spread to involve the bone if not treated in time. Therefore any ulcer of the foot should be evaluated by the doctor and infection should be treated promptly with antibiotics and wound care.
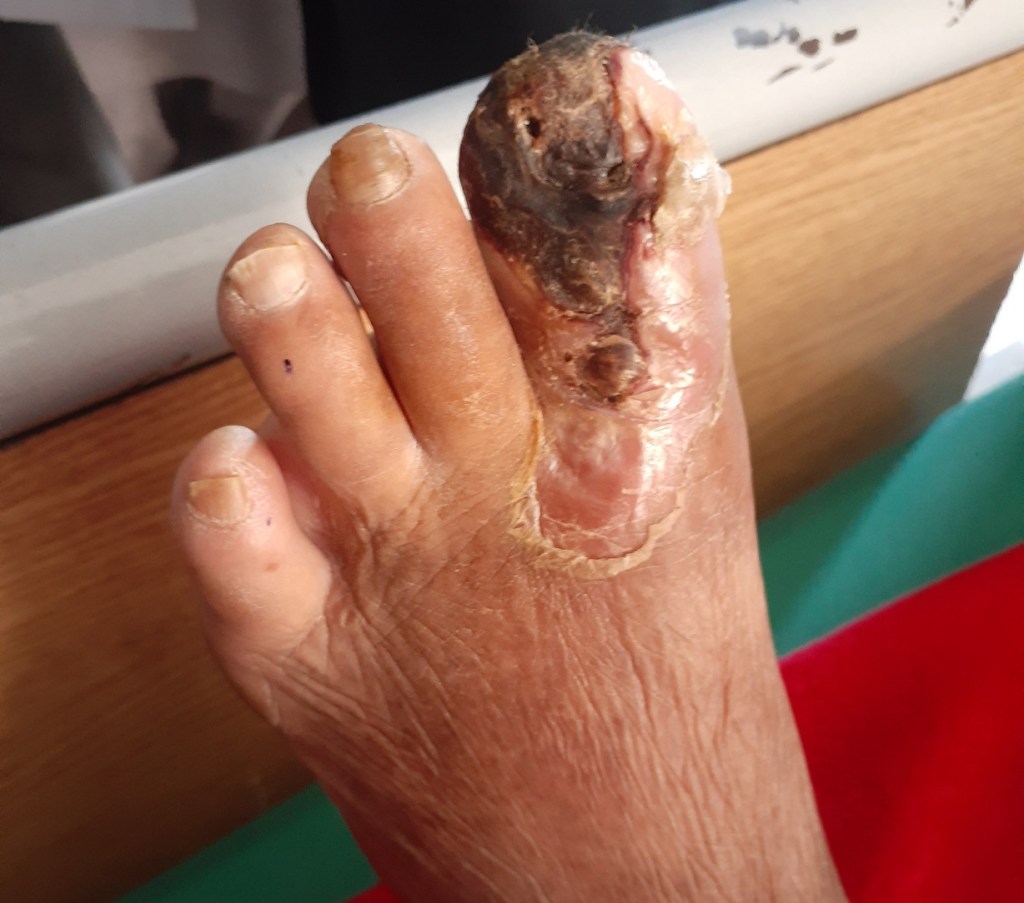
What types of infection can occur in diabetic foot?
Different studies have shown diabetic foot infections with bacteria and fungi. Gram negative, gram positive and anaerobic infections are most common. In many patients infection is poly microbial involving both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Fungal infections are also common in diabetics like tenia pedis and onychomycosis.
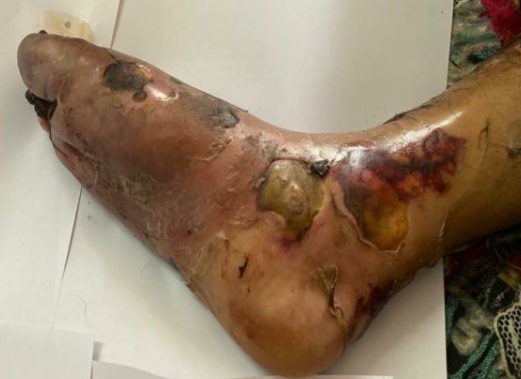
What is joint destruction or Arthopathy in diabetic foot?
Arthopathy or joint destruction is a complication of nerve damage (neuropathy) due to diabetes, the joints become soft and bone become brittle and can develop fractures, the weight bearing ability of the joint is lost and overlying skin becomes ulcerated and infected.
How gangrene develops in diabetic foot?
Gangrene will develop when blood supply to a certain area of the foot is blocked. The foot will become cold, develop blackish discoloration and necrosis, causing permanent dead tissue.
The only life saving solution in this scenario is amputation of the affected part.
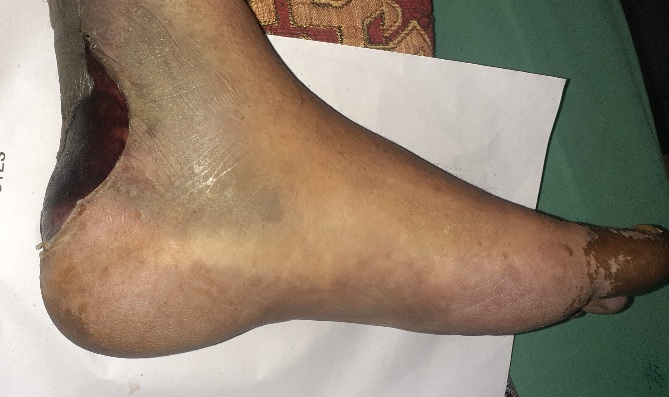
When amputation is needed in diabetic foot?
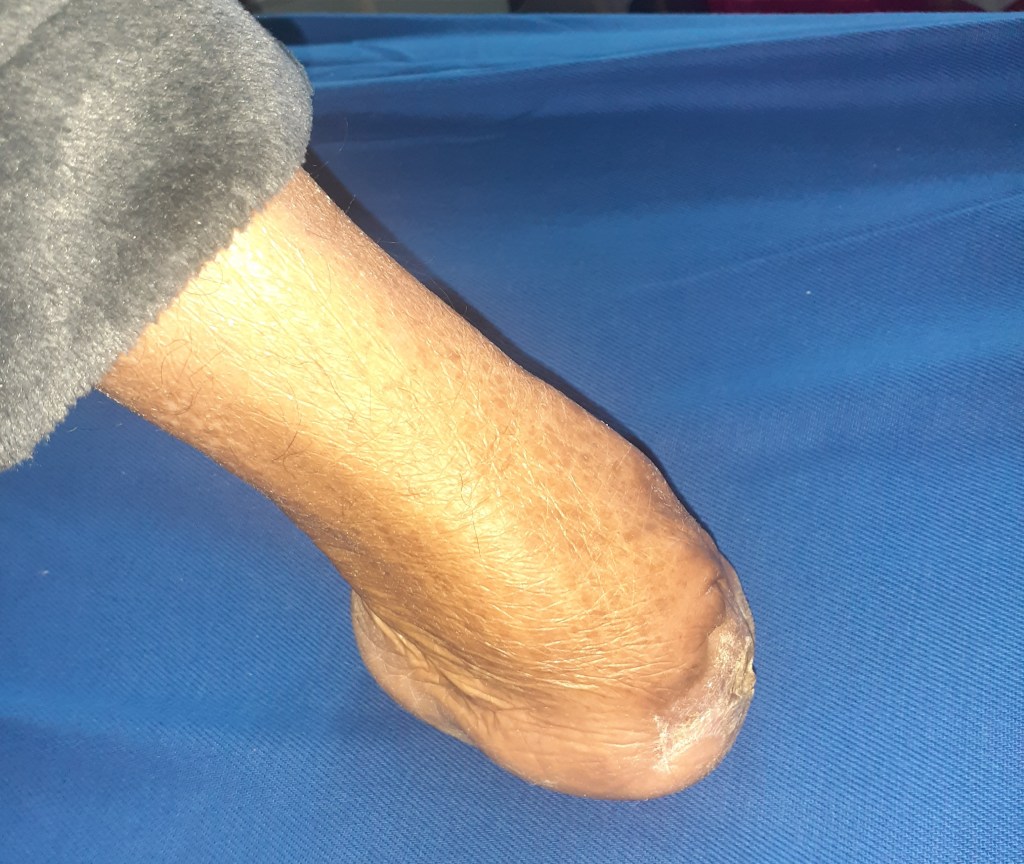
The amputation is mostly needed when the infected ulcer involves the bone and causes destruction of bone (osteomyelitis). Amputation is also needed when their is obstruction of blood supply due to vascular disease and gangrene develops.
What is diabetic foot syndrome?
Diabetic foot syndrome is defined as infection, ulceration or destruction of deep tissues of feet in a patient with diabetes.
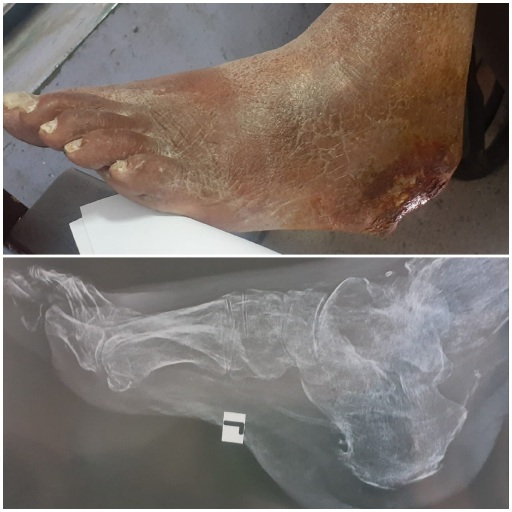
How the complications can be prevented in diabetic foot?
The only solution to prevent complications of diabetic foot is through blood sugar control and foot care.
What measures should be taken for foot care in diabetes?
The diabetic patient needs to pay special attention to feet in order to prevent the most dreaded complications. The primary management of diabetes is to achieve therapeutic goals through self care and health service support. Feet care should be practiced with daily self examination by the patient. The following tips will be helpful:
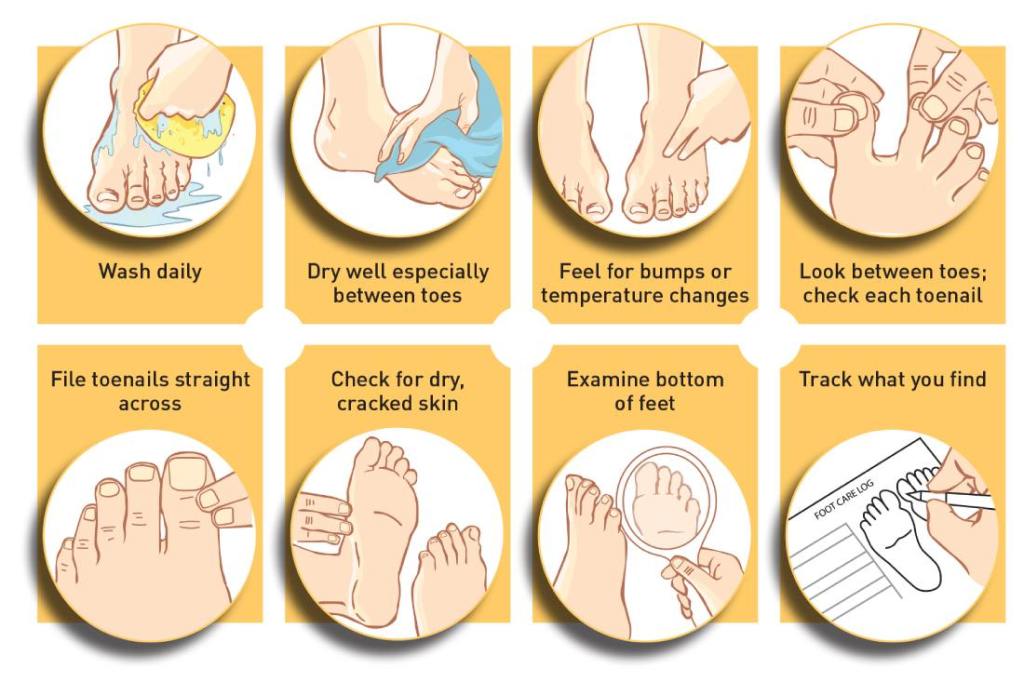
- Wash feet daily with light soap and warm water and then dry the feet and apply moisture cream or lotion.
- Do not leave interdigital spaces moist as it can lead to fungal infections.
- Daily examine the feet for minor cuts, blisters and signs of infection.
- Try to inspect heels daily for abrasions, wound.
- Cut the nails straight across to prevent ingrown toe nails.
- Wear good fitting comfortable shoes.
- Never walk bare footed.
- Do not smoke.
- High risk patients should wear properly fitting therapeutic footwear to take pressure off the feet.
How the wound of diabetic foot should be cleaned?
The foot should be soaked in warm saline or tap water and then apply antibiotic cream to keep wound moist, apply soft bandage and repeat after every 1-2 days till healing.
How gangrene can be prevented in diabetic foot?
- Blood glucose monitoring and control
- Quit smoking
- Control of Blood Pressure
- Control of lipid abnormalities
- Early detection and control of diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy.
- Care by podiatrist
What is TCC and how it can heal diabetic foot ulcers?
TCC is total contact cast, which is made of plaster or fiberglass and applied to heal non infected neuropathic and ischemic ulcers. It is considered gold standard for healing diabetic foot ulcers through off loading pressure from ulcerated area and allowing time to heal through regeneration.
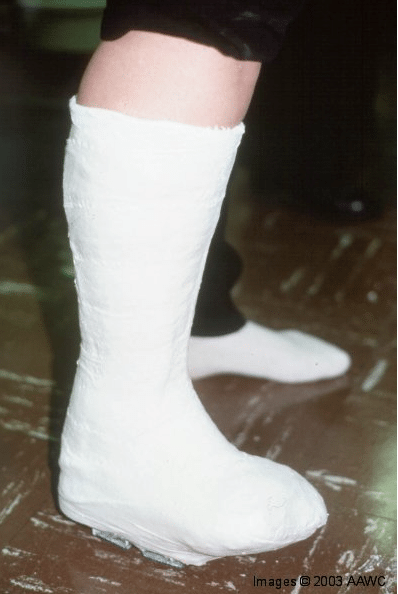
What are surgical options in management of diabetic foot?
The commonest indications for surgery in diabetic foot include:
- Debridement: Removal of infected and dead tissue to promote healing.
- Skin grafts: to reconstruct missing, weakened tissue.
- Vascular: To restore peripheral blood flow.
- Amputation: If tissue severely damaged or necrosed.
- Other surgical procedures may include shaving/ removing bone deformities that put pressure on surrounding areas including hammer toes, spurs, bunions
- Reconstruct deformities like flat foot and high arched foot.
- lengthening tendons, re-aligning, fusing deformed joints etc.
In Summary:
Management of Diabetic foot includes:
- Vascular care
- Infection care
- Pressure care
Who can help a patient with Diabetic Foot?
- Community health provider
- physician/ Endocrinologist
- Podiatrist
- Surgeon


